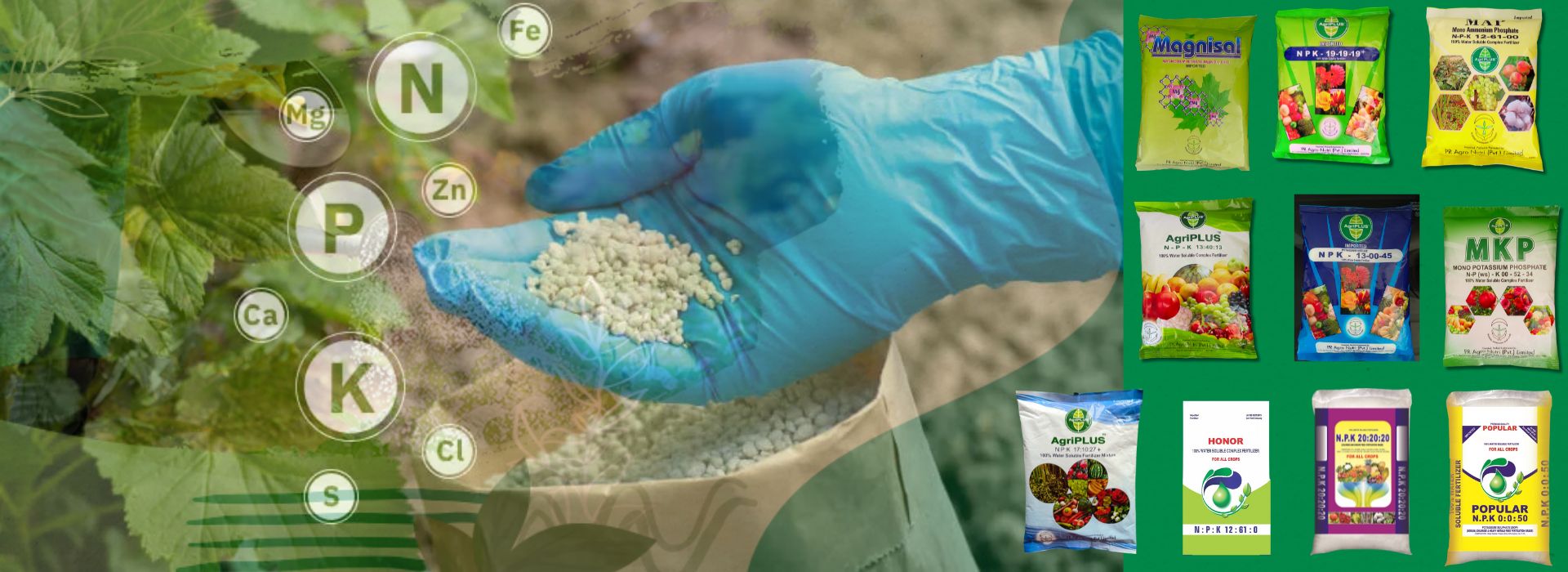
All About NPK Fertilizers: Organic, Inorganic, and Water-Soluble Options
June 16, 2025All About NPK Fertilizers: Organic, Inorganic, and
Water-Soluble Options
Fertilizers are the lifeblood of modern agriculture, and
among the most essential are NPK fertilizers. These fertilizers supply
the three critical nutrients that plants need to grow: Nitrogen (N),
Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K). Whether you're a small-scale gardener or
a large-scale farmer, understanding the types of NPK fertilizers—organic,
inorganic, and water-soluble—can help you make better decisions for soil
health, plant growth, and crop yield.
🌿 What Is NPK?
- Nitrogen
(N) promotes
leafy growth.
- Phosphorus
(P) supports
strong root development and flowering.
- Potassium
(K) enhances
overall plant health and resistance to disease.
An NPK fertilizer label like 20-20-20 means it
contains 20% of each nutrient by weight.
🌱 Types of NPK Fertilizers
1. ✅ Inorganic NPK Fertilizers
Also called chemical or synthetic fertilizers, these
are manufactured using mineral salts and chemical processes.
Pros:
- Quick
nutrient release
- Precise
NPK ratios
- Cost-effective
and widely available
Cons:
- Overuse
can degrade soil health
- May
cause nutrient runoff into water bodies
- Doesn't
improve soil structure
Examples:
- DAP
(Di-Ammonium Phosphate)
- Urea
+ MOP/SSP combinations
- Complex
NPK blends like 10-26-26 or 19-19-19
2. 🌾 Organic NPK Fertilizers
Derived from natural sources like compost, manure, bone meal,
and seaweed.
Pros:
- Improves
soil fertility and structure
- Releases
nutrients slowly and sustainably
- Enhances
microbial activity in the soil
Cons:
- Slower
nutrient release
- NPK
ratios may not be precise
- Requires
larger quantities
Examples:
- Vermicompost
- Poultry
litter
- Organic
NPK granules with certified inputs
3. 💧 Water-Soluble NPK Fertilizers
These dissolve completely in water and are ideal for fertigation
(fertilizer via irrigation) and foliar application.
Pros:
- Immediate
nutrient availability
- Suitable
for high-value crops (horticulture, greenhouse)
- Easily
absorbed through roots and leaves
Cons:
- Requires
careful handling and dosage
- Slightly
more expensive than conventional types
Examples:
- 19-19-19
(General purpose)
- 13-40-13
(Flowering stage)
- 00-52-34
(Fruit development stage)
🌾 When and How to Use NPK Fertilizers
- Soil
Testing: Always
test your soil to determine the right type and quantity of fertilizer.
- Growth
Stage: Young
plants need more nitrogen, while mature crops require more phosphorus and
potassium.
- Application
Method: Choose
between broadcasting, top dressing, foliar spray, or fertigation based on
crop type.
🌎 Sustainable Use of NPK Fertilizers
To maximize crop yield without harming the environment,
adopt Integrated Nutrient Management (INM):
- Combine
organic and inorganic inputs
- Use
biofertilizers like Azospirillum, Rhizobium, or Mycorrhiza
- Monitor
and adjust based on soil health and crop response
🧪 Final Thoughts
NPK fertilizers, in their various forms, play a critical role
in agriculture. While inorganic fertilizers offer speed and precision, organic
options build long-term soil health, and water-soluble types provide
targeted efficiency. The best choice often depends on your crop, soil,
climate, and farming goals.
By choosing the right NPK fertilizer and using it wisely, you
can ensure better plant growth, improved yield, and a sustainable future for
your farm.
At krishibazaar.in, you
can find and buy various agricultural products. For agricultural guidance on
selecting the most suitable products for your crops, please contact or WhatsApp
at +917887880887.





Guest reviews
No reviews found for this Blog