Maximizing Soybean Yields: Best Practices for Planting and Cultivation
September 16, 2024Maximizing
Soybean Yields: Best Practices for Planting and Cultivation
Soybeans are
a versatile and highly profitable crop, cultivated widely for their uses in
food, feed, and industrial products. With the right planting and cultivation
practices, soybean farmers can significantly enhance their yields and overall
productivity. In this guide, we’ll explore the best practices for growing
soybeans, from land preparation to harvesting, to help you achieve optimal
results.
1.
Choosing the Right Soybean Variety
The first
step in growing soybeans is selecting the right variety suited to your region’s
climate and soil conditions. Factors to consider when choosing a variety
include:
- Maturity Group: Different soybean varieties
are grouped based on their maturity time. Selecting the right maturity
group for your growing zone ensures that your soybeans will fully develop
within the available growing season.
- Disease Resistance: Look for varieties that are
resistant to common diseases such as Phytophthora root rot, soybean cyst
nematode, and brown stem rot. This helps minimize the risk of crop losses.
- Yield Potential: High-yielding varieties that
suit local growing conditions can significantly boost productivity and
profitability.
2.
Preparing the Land for Soybean Planting
Proper land
preparation is essential to ensure healthy root development and effective
nutrient uptake. Follow these steps for optimal soil conditions:
- Soil Testing: Conduct a soil test to check
for nutrient levels and pH. Soybeans grow best in soils with a pH range of
6.0 to 7.0. Based on the test results, apply the necessary amendments,
such as lime, to correct pH imbalances.
- Tillage: Prepare the soil by using
either conventional tillage or reduced/no-till methods, depending on your
farm's setup. While conventional tillage breaks up compacted soil, no-till
practices help preserve soil structure and moisture, reducing erosion.
- Weed Control: Before planting, clear the
field of weeds that could compete with soybeans for nutrients and
sunlight. Using herbicides or cover crops during the off-season can help
suppress weed growth.
3.
Optimal Planting Time for Soybeans
Timing your
soybean planting is critical for maximizing yields. Soybeans are sensitive to
both temperature and day length, so planting too early or too late can affect
plant growth and development.
- Soil Temperature: Soybeans should be planted
when the soil temperature reaches at least 50°F (10°C) at a depth of 2
inches. This ensures proper seed germination and early growth.
- Planting Window: The ideal time to plant
soybeans is in the late spring or early summer, depending on your
location. Planting too early, when temperatures are still cool, can slow
growth, while late planting may reduce yields due to shorter growing
seasons.
4.
Planting Techniques for Soybeans
To ensure
healthy, uniform growth, follow these best practices during planting:
- Row Spacing: Soybeans can be planted in row
spacings between 15 and 30 inches. Narrow rows tend to increase yields by
allowing plants to form a canopy earlier, reducing weed competition and
capturing more sunlight.
- Seeding Rate: The recommended seeding rate
for soybeans typically ranges from 100,000 to 140,000 seeds per acre,
depending on row spacing and the variety used. Ensure uniform planting
depth (1 to 1.5 inches) for consistent germination.
- Inoculation: Soybeans form a symbiotic
relationship with rhizobia bacteria to fix nitrogen from the air. If
soybeans haven’t been grown in the field recently, inoculating seeds with
the appropriate bacteria can enhance nitrogen fixation and boost crop
health.
5.
Fertilization and Nutrient Management
Although
soybeans fix nitrogen from the atmosphere, they still require other nutrients
for optimal growth, including phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients like
sulfur, magnesium, and boron.
- Phosphorus and Potassium: Apply these nutrients based on
soil test recommendations. Phosphorus promotes root development and
flowering, while potassium enhances disease resistance and water
efficiency.
- Micronutrients: Micronutrient deficiencies can
limit growth, especially in sandy or low-organic soils. Use foliar
applications or soil-applied fertilizers to address deficiencies.
- Crop Rotation: Rotate soybeans with
non-legume crops like corn or wheat to maintain soil health and reduce the
risk of disease buildup.
6.
Irrigation and Water Management
Soybeans
need consistent moisture, especially during critical growth stages such as
flowering and pod filling. Here are some tips for effective water management:
- Monitor Moisture Levels: Soybeans require about 1 to
1.5 inches of water per week. Use soil moisture sensors or visual
inspection to monitor water availability and avoid over- or
under-watering.
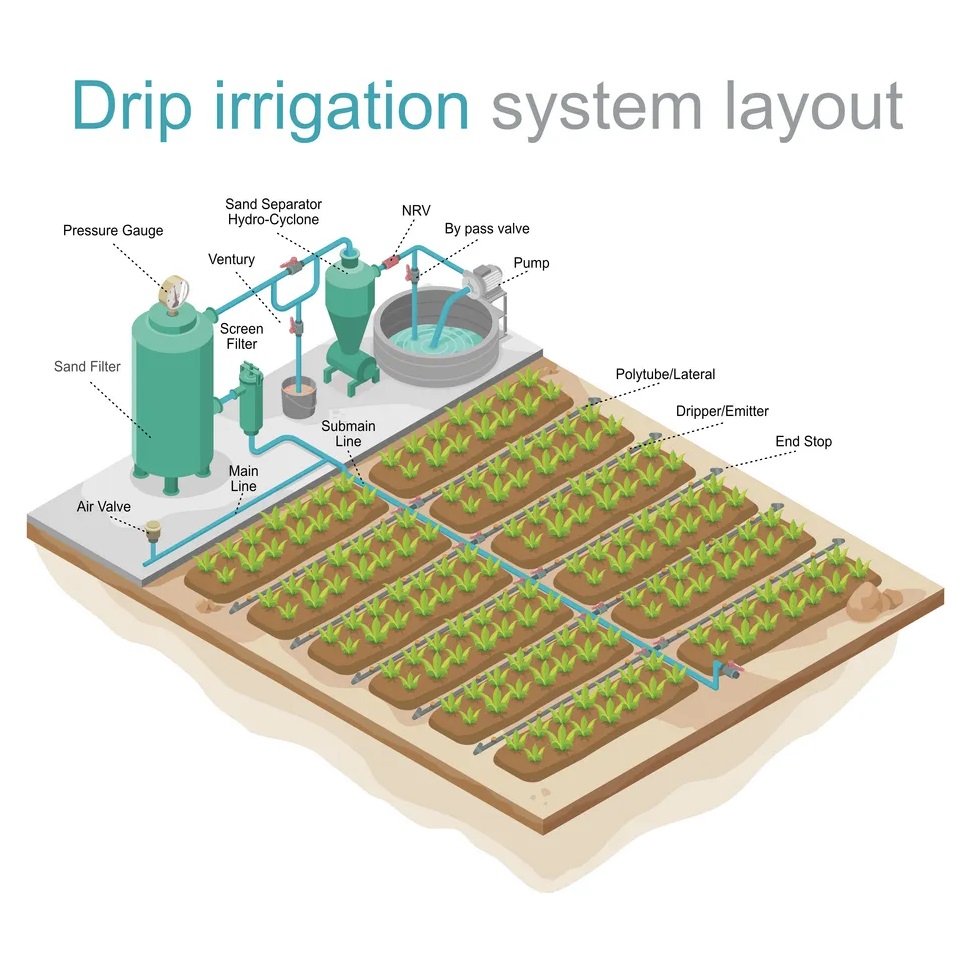
- Irrigation Methods: Drip irrigation or sprinkler
systems are ideal for delivering water directly to the root zone,
minimizing waste. In areas with sufficient rainfall, supplemental
irrigation may only be needed during dry spells.
- Drainage: Ensure that your fields have
proper drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can suffocate roots and
lead to disease.
7. Pest
and Disease Control
Soybeans are
susceptible to various pests and diseases, which can significantly reduce
yields if not properly managed.
- Pests: Common soybean pests include
aphids, soybean loopers, and cutworms. Use integrated pest management
(IPM) techniques, including scouting, natural predators, and targeted
insecticides, to keep pest populations under control.
- Diseases: Diseases such as soybean rust,
white mold, and sudden death syndrome can devastate crops. Plant
disease-resistant varieties and rotate crops to reduce disease pressure.
Fungicide applications may be necessary in severe cases.
8. Weed
Management
Weed
competition can severely limit soybean growth, especially during the early
stages of development. Effective weed control strategies include:
- Pre-Emergence Herbicides: Apply herbicides before
planting to prevent early weed growth. This reduces competition during the
critical early development stages of soybeans.
- Post-Emergence Herbicides: If weeds emerge during the
growing season, apply post-emergence herbicides to control broadleaf and
grass weeds.
- Cultural Practices: Practices like cover cropping,
mulching, and narrow row spacing help reduce weed growth by shading the
soil and limiting available resources for weeds.
9.
Harvesting Soybeans
The timing
and method of harvesting soybeans can significantly impact yield and seed
quality. Follow these practices to ensure a successful harvest:
- Harvest Timing: Soybeans are ready to harvest
when the pods turn brown and the leaves have fallen off. The moisture
content of the seeds should be between 13-15% at harvest to avoid damage
during storage.
- Harvesting Equipment: Use a combine harvester for
efficient harvesting. Ensure the machine is properly calibrated to avoid
seed loss or damage.
- Post-Harvest Handling: Store harvested soybeans in
dry, cool conditions to prevent spoilage. Proper storage helps maintain
seed quality and market value.
Conclusion:
Best Practices for High-Yield Soybeans
Growing
soybeans can be highly rewarding when proper planting and cultivation
techniques are followed. By selecting the right variety, preparing the soil,
managing nutrients, and controlling pests, farmers can optimize their soybean
yields. Adopting these best practices not only enhances productivity but also
contributes to sustainable agriculture by maintaining soil health and reducing
environmental impacts.
At krishibazaar.in,
you can find and buy various agricultural products. For agricultural guidance
on selecting the most suitable products for your crops, please contact or
WhatsApp at +917887880887





Guest reviews
No reviews found for this Blog